The guiding principle of innovation procurement is to “begin with small taregets and rapidly expand.” Introducing this approach is often most effective when implemented as a gradual learning process. This means that the necessary changes for innovation procurement, whether they involve cultural shifts or procedural adjustments, do not have to occur all at once. A successful innovation project can be initiated from the grassroots level, starting with addressing simple, practical issues.
To initiate this process, one can start by identifying areas such as environment/climate change or healthcare that require attention and could benefit from innovative solutions. The initial emphasis should be on sectors and projects where innovation can be more easily integrated and can yield the most significant impact. By commencing with small projects, trust and confidence can be built, laying the foundation for the attraction of larger, more complex projects in the future.
Advantages of Innovation Procurement
Advantages of employing innovation procurement – for procurers
- Enhancement of service modernization, efficiency, and quality.
- Provision of solutions tailored to specific, unmet needs or challenges.
- Potential for short and/or long-term cost reduction.
- Capability to discern market trends and discover novel solutions aligning with customer requirements.
- Exposure to a broader range of suppliers.
- Acquisition of knowledge and methodologies applicable to other projects.
- Chance to gain positive publicity and enhance reputation.
Advantages of employing innovation procurement – for suppliers
- Access to significant public sector clientele.
- Insight into challenges and priorities within the public sector.
- Opportunities for research, development, and commercialization of solutions.
- Potential to secure future contracts and enter new markets.
- Possibility of positive publicity.
- Chance to reinforce competencies and human capital capacity.
Innovation procurement approaches
There are two approaches to the innovation procurement, which are used for different needs and situations.
Pre-commercial procurement (PCP) is utilized in situations when:
- it is crucial in the early stages to select multiple suppliers to identify the most suitable candidates for subsequent prototyping and testing stages.
- is necessary to diminish investment risks and enhance competitiveness by fostering the development of superior products.
- first test samples are created, and an innovation procurement procedure is implemented, and it is evaluated both by price and quality criteria.
On the other hand, Innovation procurement procedures are opted for when:
- There is a need to significantly minimize time invested in research and development (R&D).
- It is particularly useful for acquiring a product or solution that is not currently available in the market.
- It is imperative to incorporate the development of a prototype into the procurement contract.
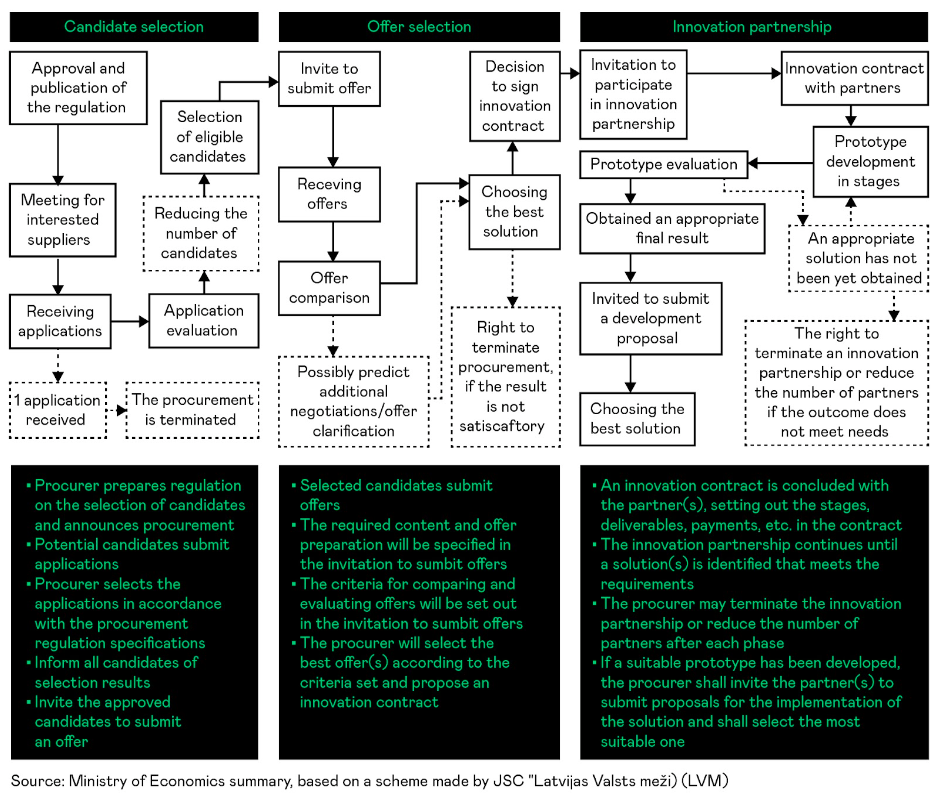
Innovation partnership procedure
Before establishing an innovation partnership procedure, it’s crucial to gain insights into the relevant market through activities like initiating prior consultations with potential suppliers. The customer should articulate their needs precisely, enabling market participants to comprehend the problem’s nature, associated risks, and the opportunities for engagement. Public procurement regulations permit the formation of contracts with multiple innovation partners, deferring the final selection of deliverables throughout the contract duration. This approach facilitates the support of various innovative solutions, with the flexibility to choose one or more suppliers for implementation. Given the fact that innovation is intellectual property, careful consideration of intellectual property matters.
Innovation partnership procedure
Pre-procurement market consultations
- Engaging in pre-procurement market consultations with industry players aims to conduct a comprehensive market analysis by directly gathering information from potential suppliers of innovative solutions.
- This process is particularly crucial for intricate procurement endeavors, where the customer may find it challenging to independently assess the technical, financial, and resource viability of the planned procurement.
- Using insights gleaned from these consultations, the contracting authority can refine the procurement specifications and determine the most suitable procurement procedure. Additionally, the authority can verify whether a viable solution already exists based on the information gathered during the consultation.
- Market research and guidance can take various forms, including:
- digital consultations facilitated through a platform connecting authorities with entrepreneurs,
- face-to-face counseling through events, or unconventional methods such as competitions, hackathons, or idea workshops.
- Telephonic counseling, involving structured interviews conducted by a third party to ensure impartiality, is also a viable approach.
Innovation procurement and Intellectual property
In the case of innovation procurement, the procurer will often face questions about intellectual property rights that need to be addressed in the technical specification and the contract. At the stage of defining the need and planning the procurement, it should be considered whether and how these rights will be transferred as a result of the innovation. It is important not only to specify the exact terms and conditions of the acquisition, but also to carefully assess the future potential of the innovation, which includes the transfer of intellectual property rights to the procurer or their retention by the supplier.
Green Public Procurement
Green Public Procurement (GPP) is a tool for environmental policy that may be used to systematically integrate environmental (including social) conditions into all operations linked to the procurement of goods or services:
- Minimise environmental effects: every good (or service) you buy has an environmental impact at all stages of its life cycle (production – use – recycling for reuse or disposal in landfill);
- Encourage social improvements: better working conditions, through conditions built into the procurement procedure;
- Save money by planning purchases: when planning to buy a good or service, real needs are assessed first, thus reducing the volume of purchases. Secondly, an assessment of the life cycle costs of the product is made. In this way, all factors can be taken into account (not only the initial price of the good or service, but also the operating and waste management costs) and ultimately savings can be achieved.
Socially Responsible Public Procurement
Additionally, ethical and responsible buying encourages companies to manage their labour and production process more sustainably and responsibly. Therefore, Socially Responsible Public Procurement is a tactical instrument that successfully advances labour and social policy.
In Socially Responsible Public Procurement (SRPP), the procuring entity not only purchases a good or service, but also creates a positive social impact, for example:
- purchasing goods made ethically;
- giving jobs to people who have left the workforce;
- enhancing working conditions for employees;
- requiring that those employed in the service provision undergo training;
- guaranteeing that workers receive wages commensurate with the labour market (sectoral agreements);
- and providing opportunities for small and medium-sized businesses, including social enterprises, to engage in public procurement.
















